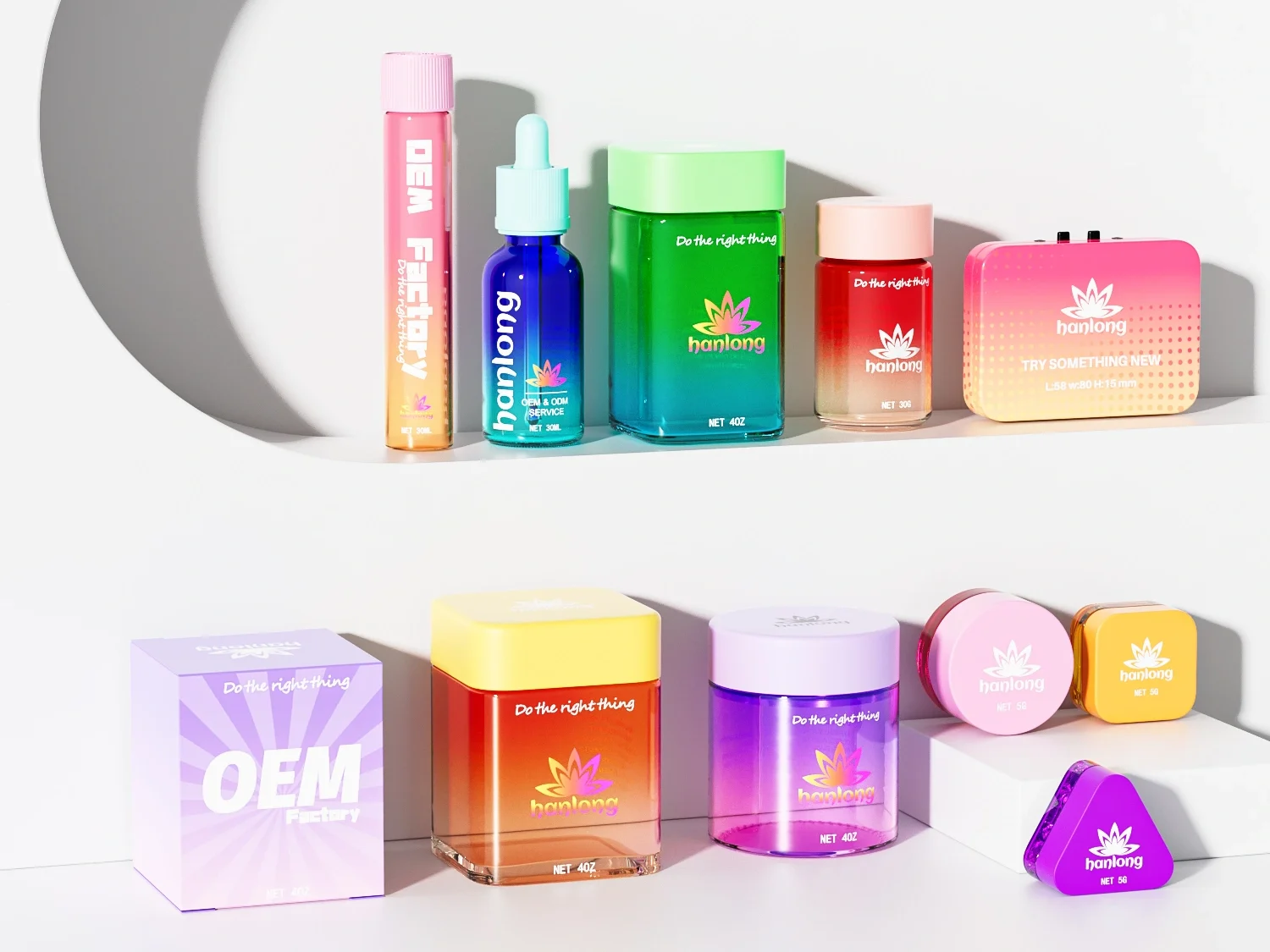
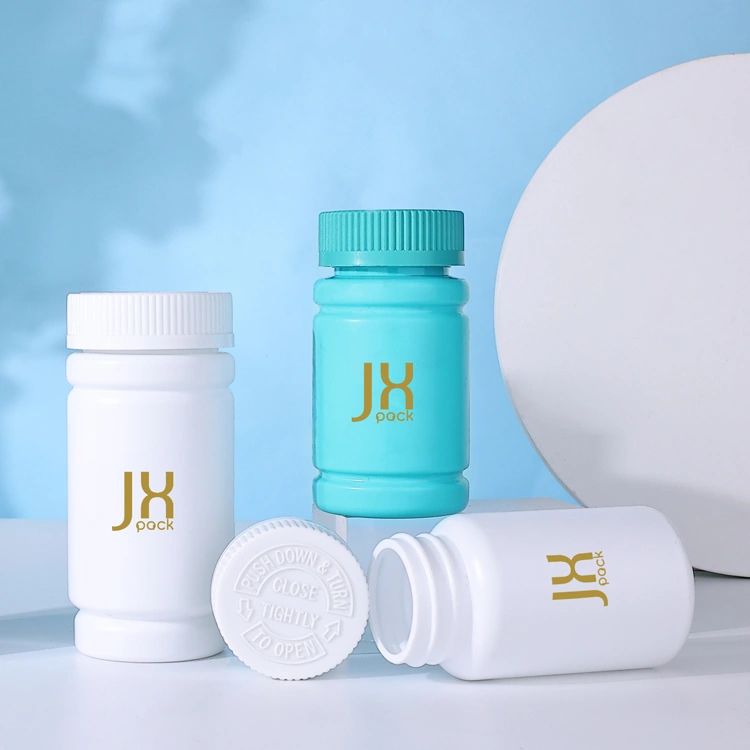
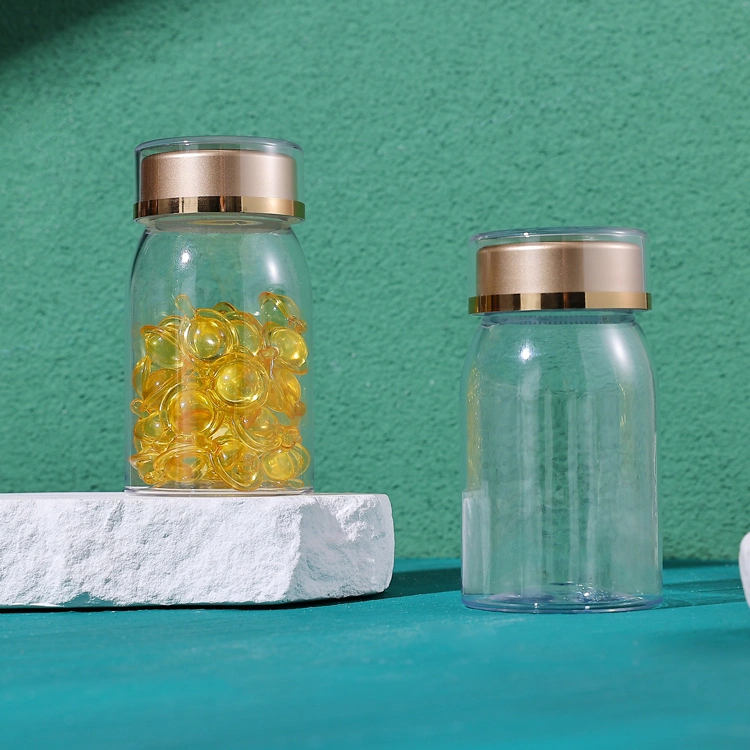
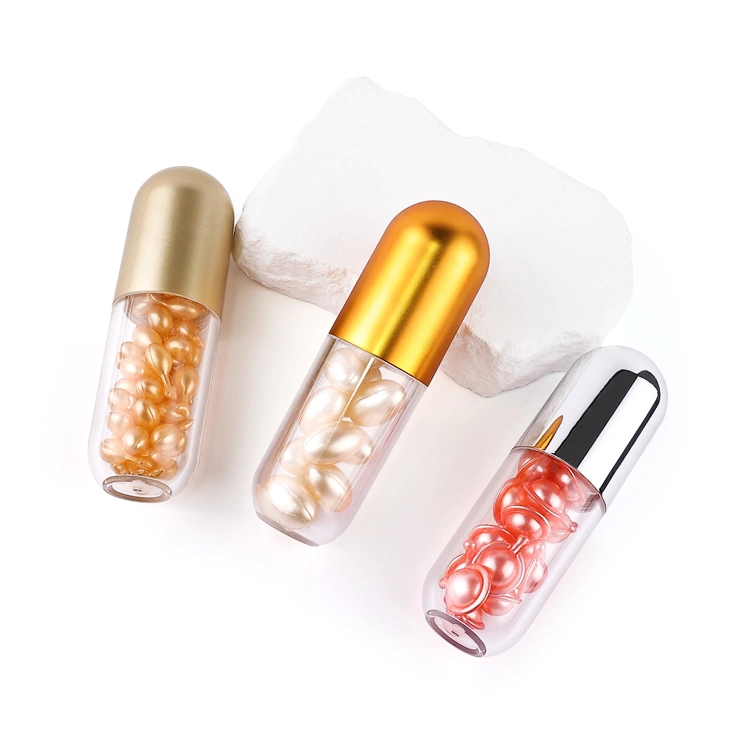
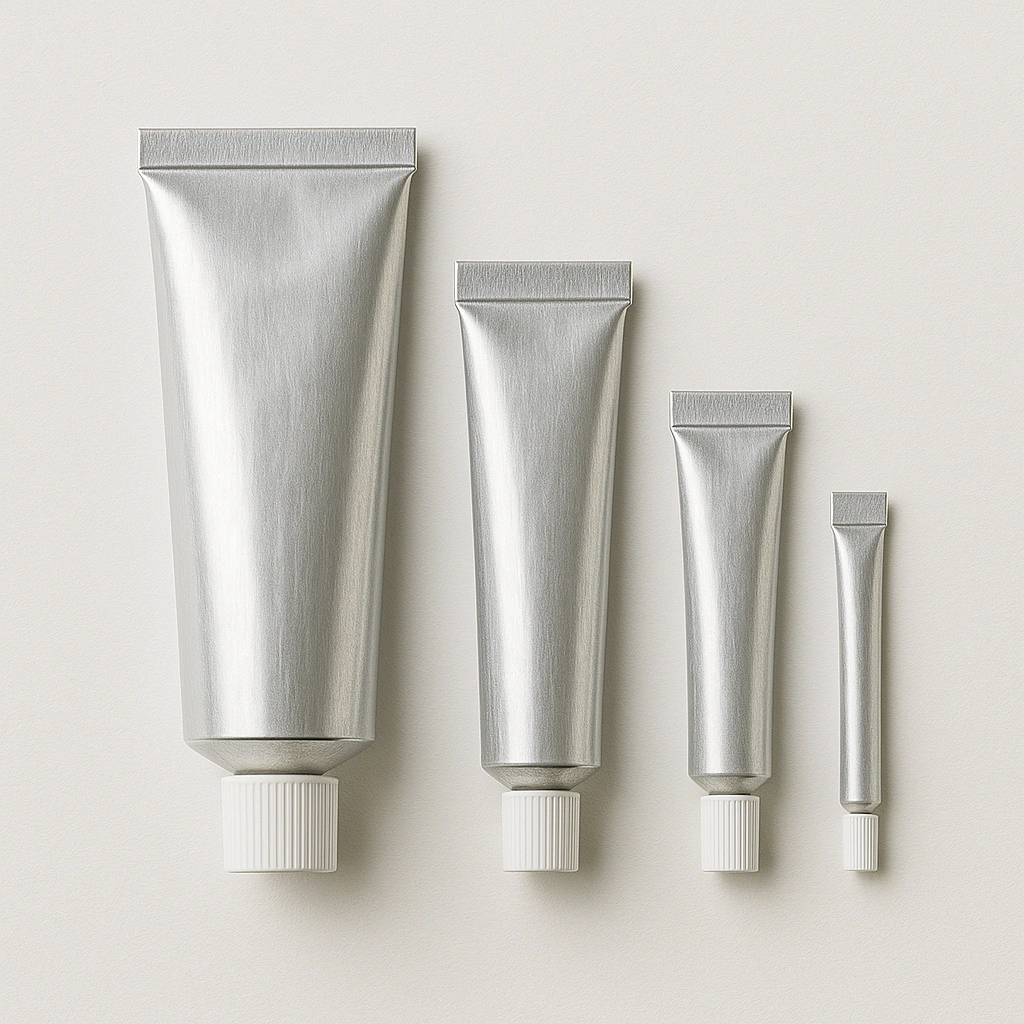
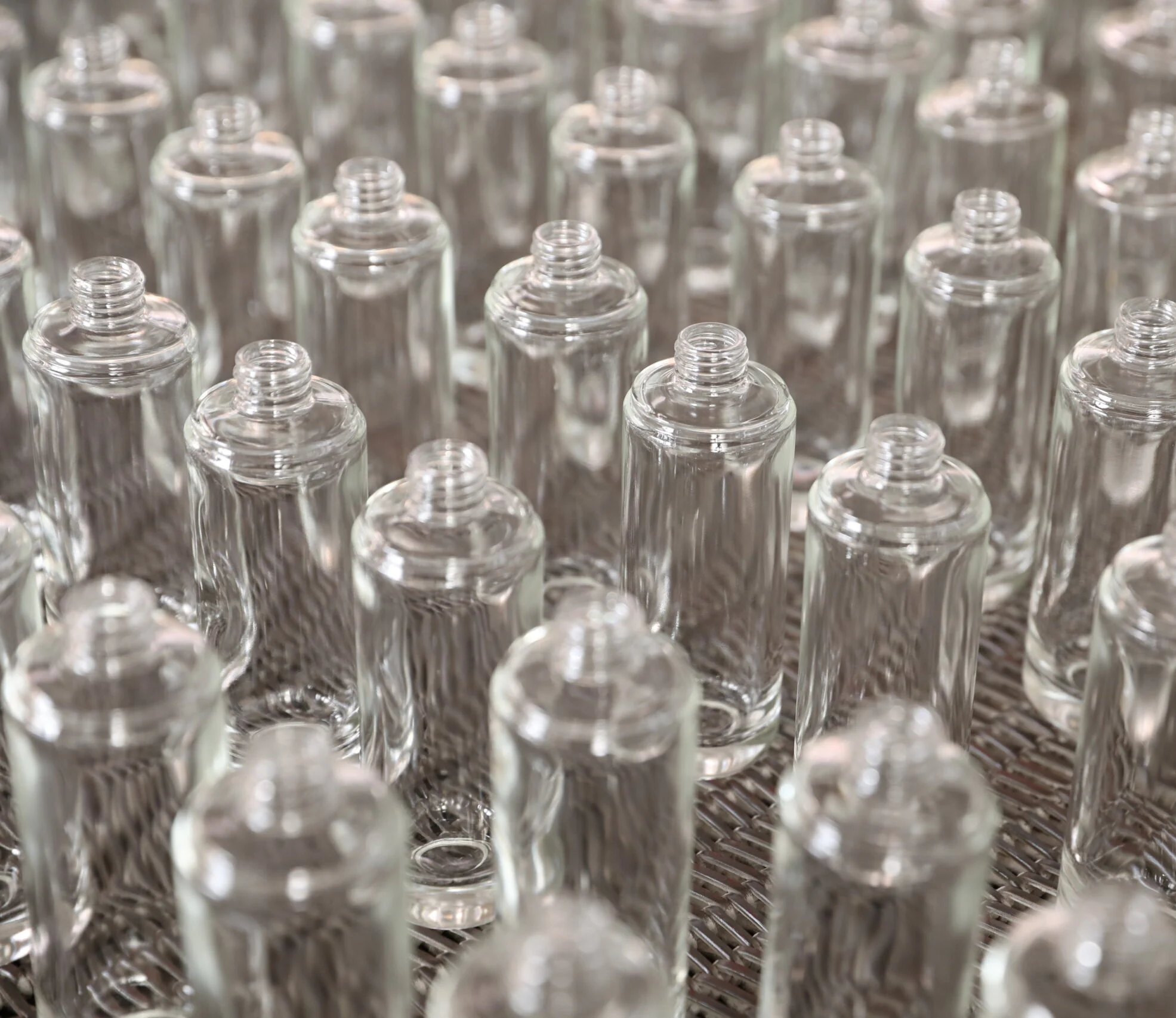
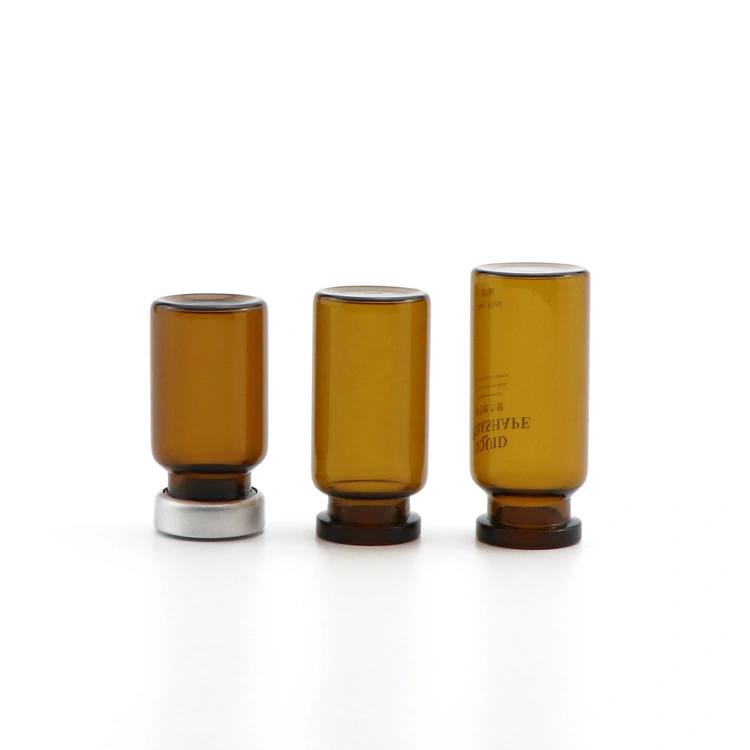
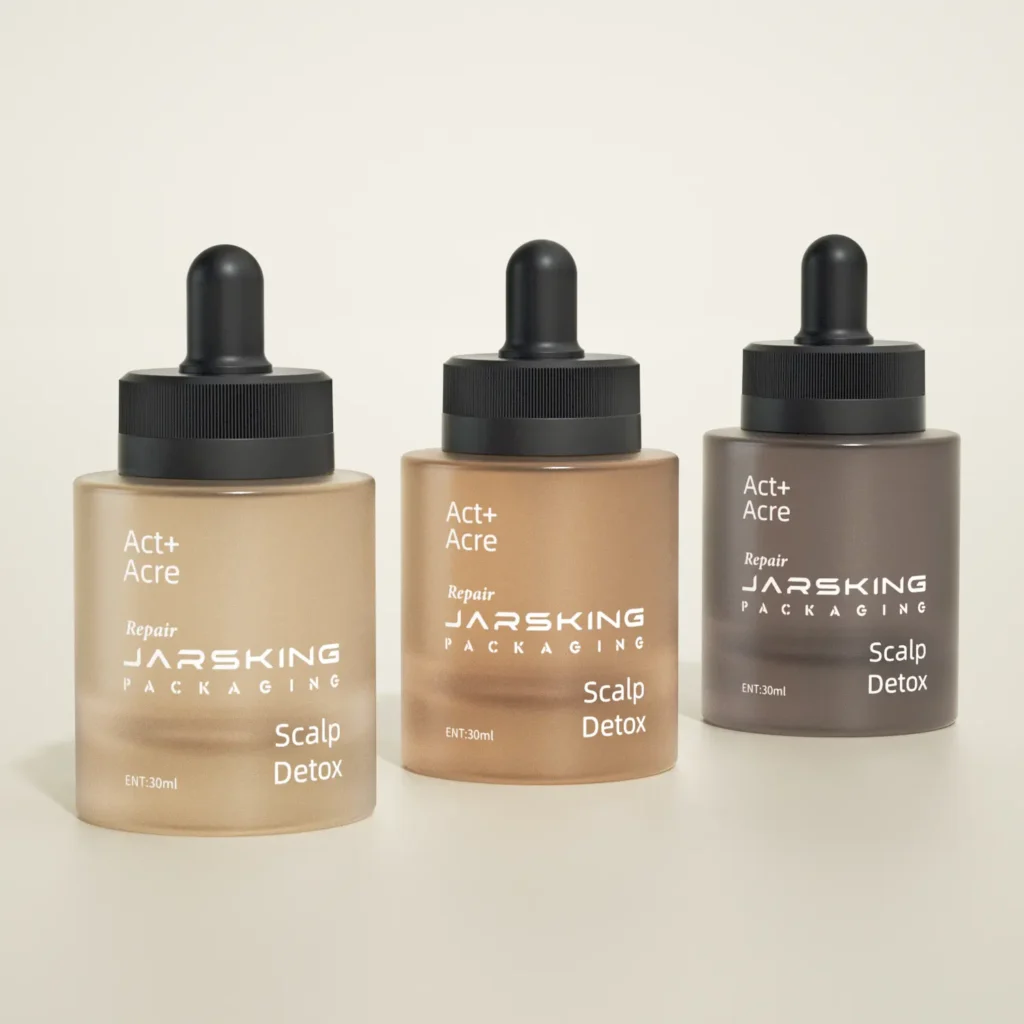
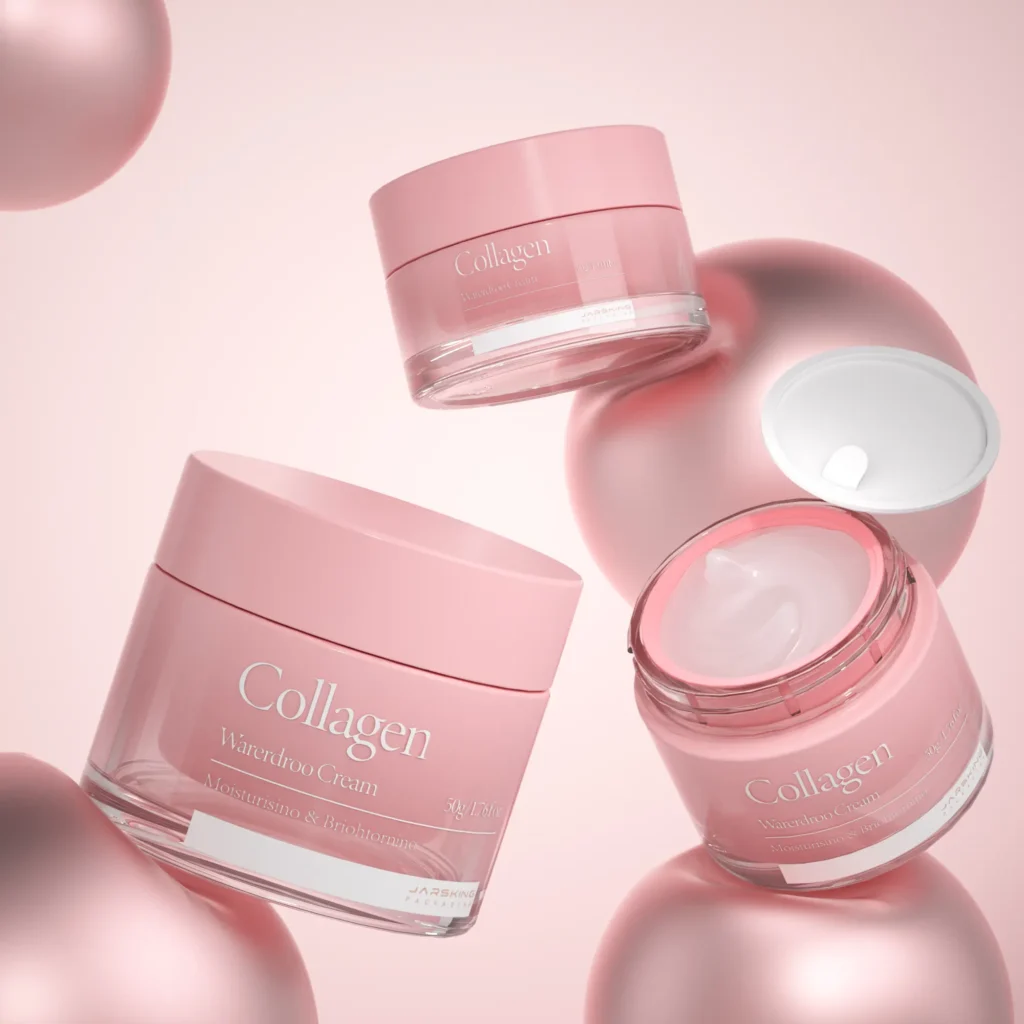
· LATEST DESIGN
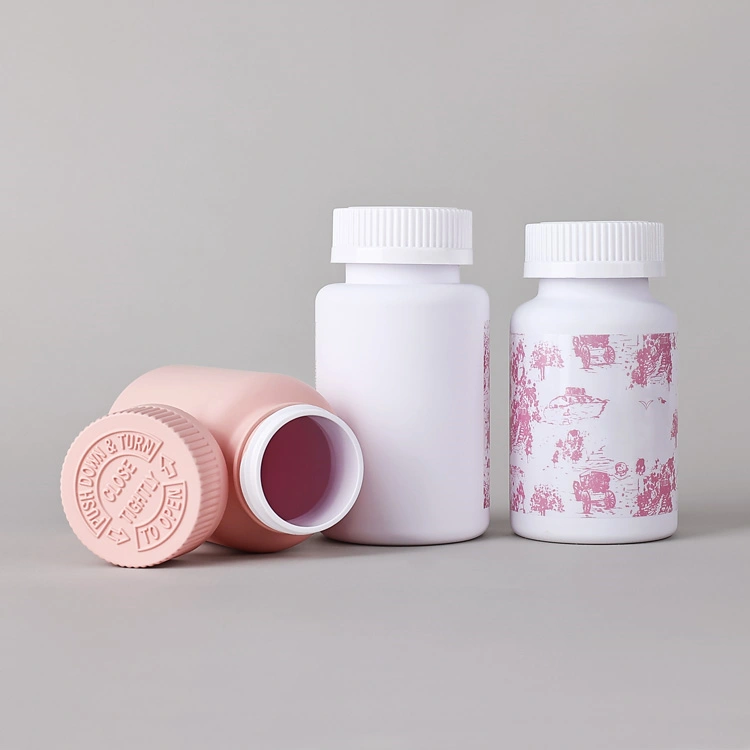
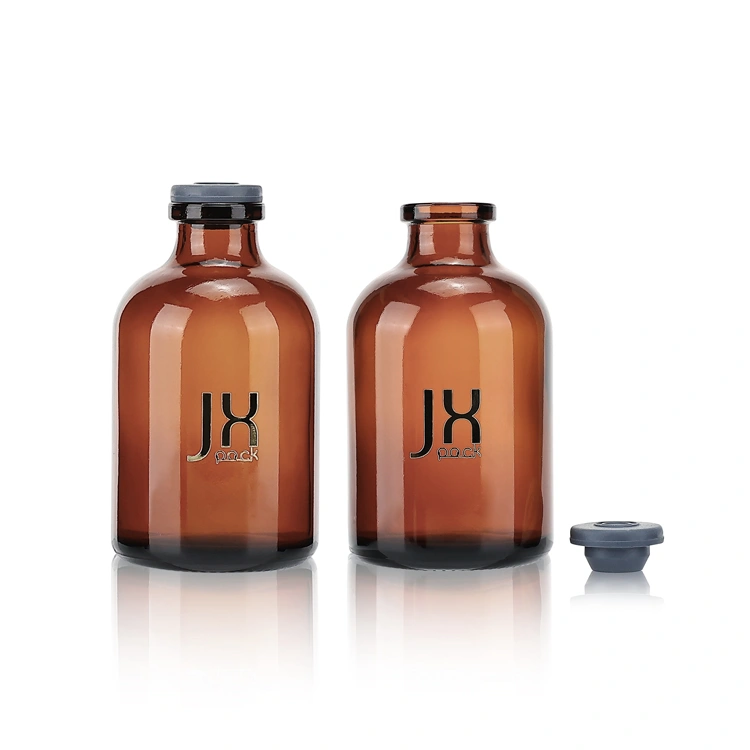
· LATEST DESIGN
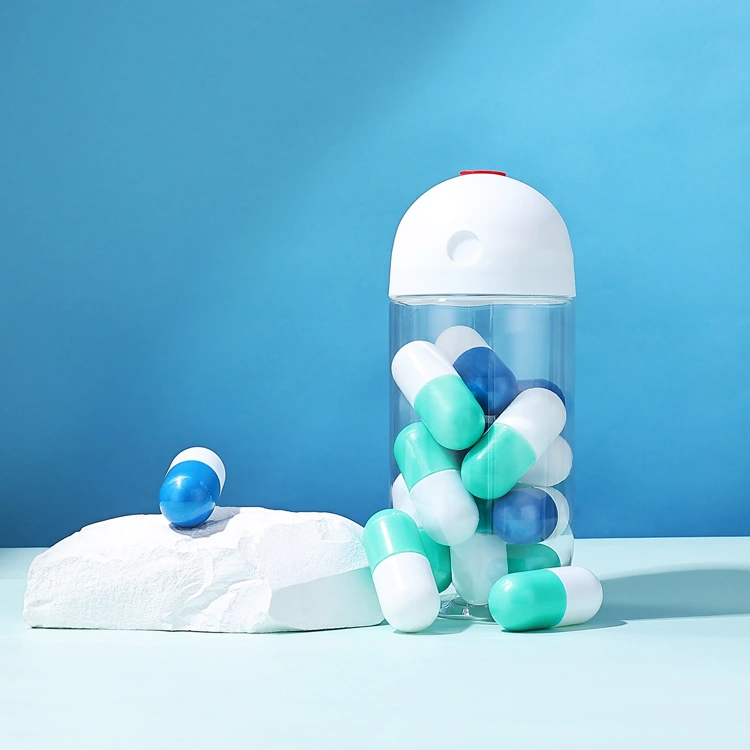
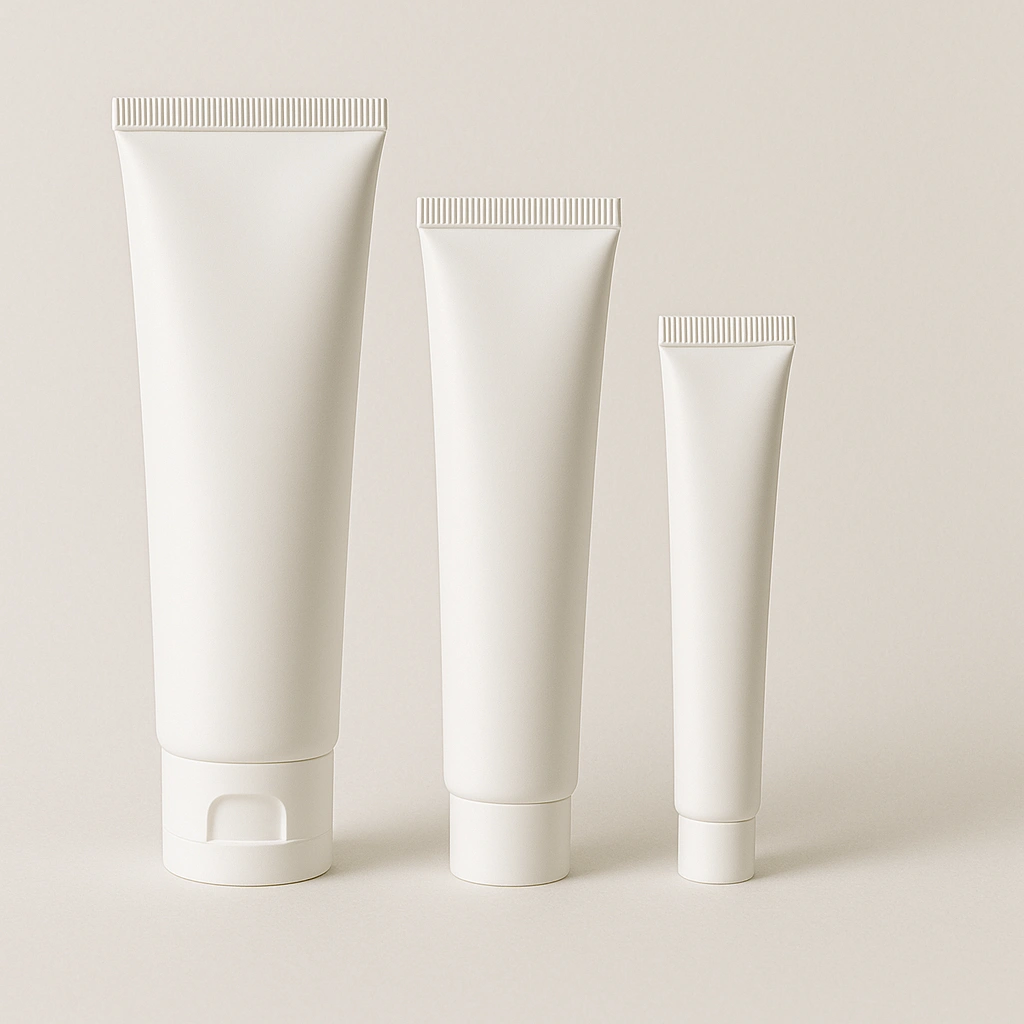
· LATEST DESIGN
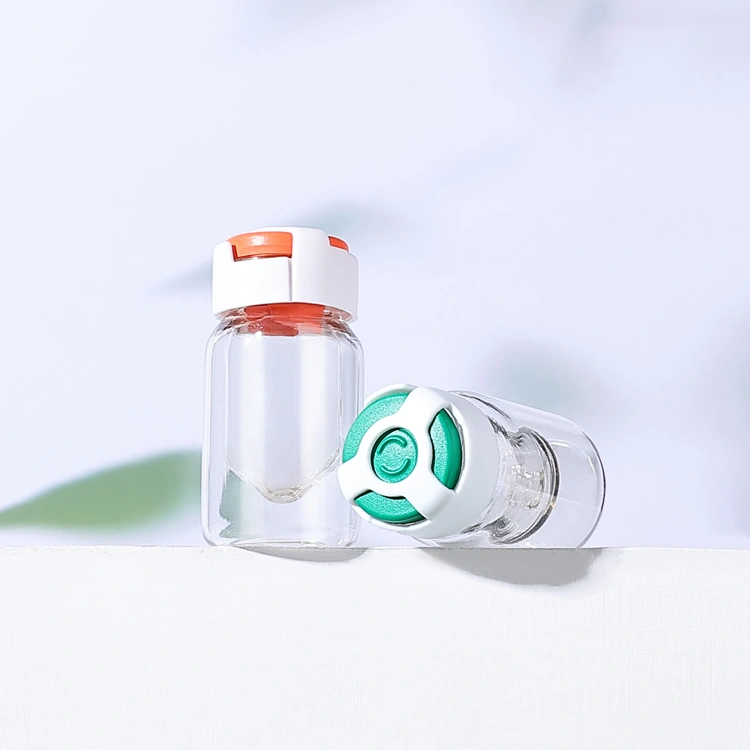
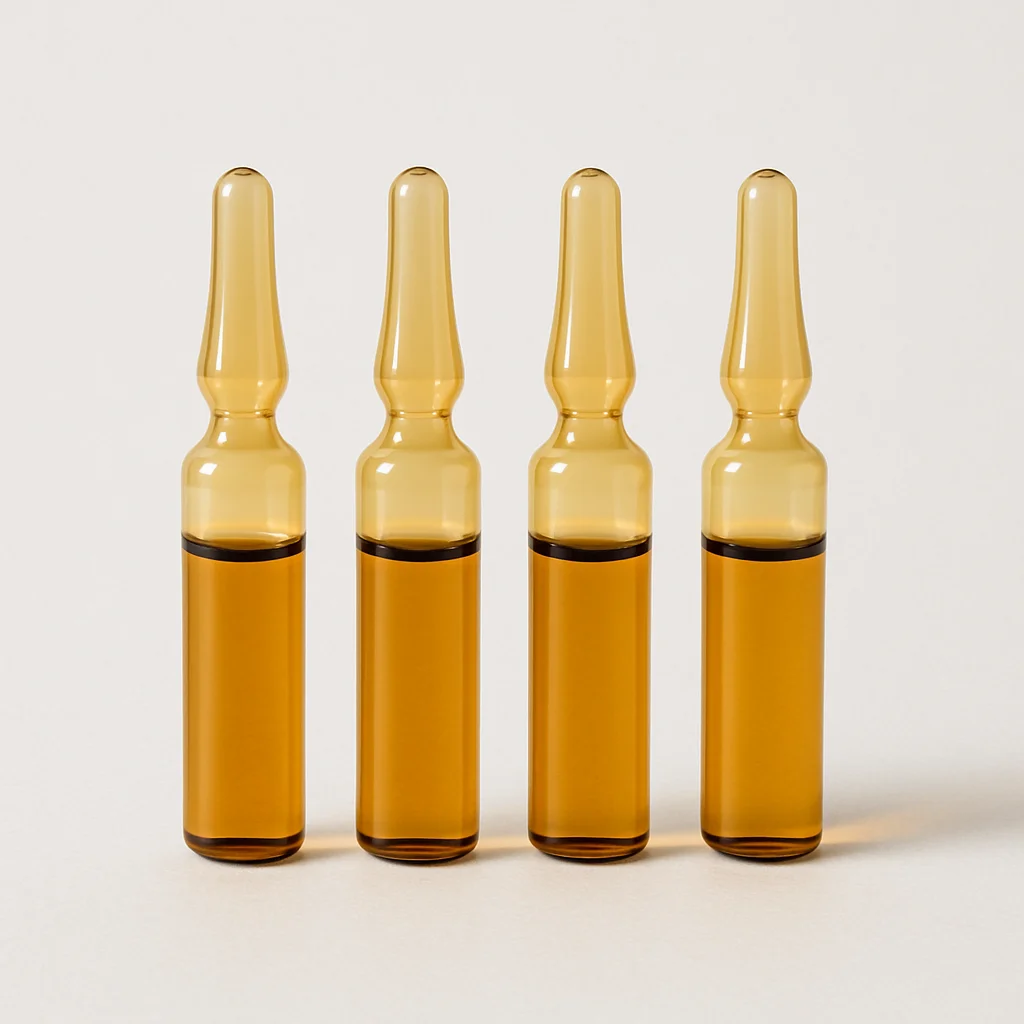
· LATEST DESIGN
Jarsking covers all cosmetics,cannabis and perfume markets. Ask custom solutions here!
· EFFICIENCY+
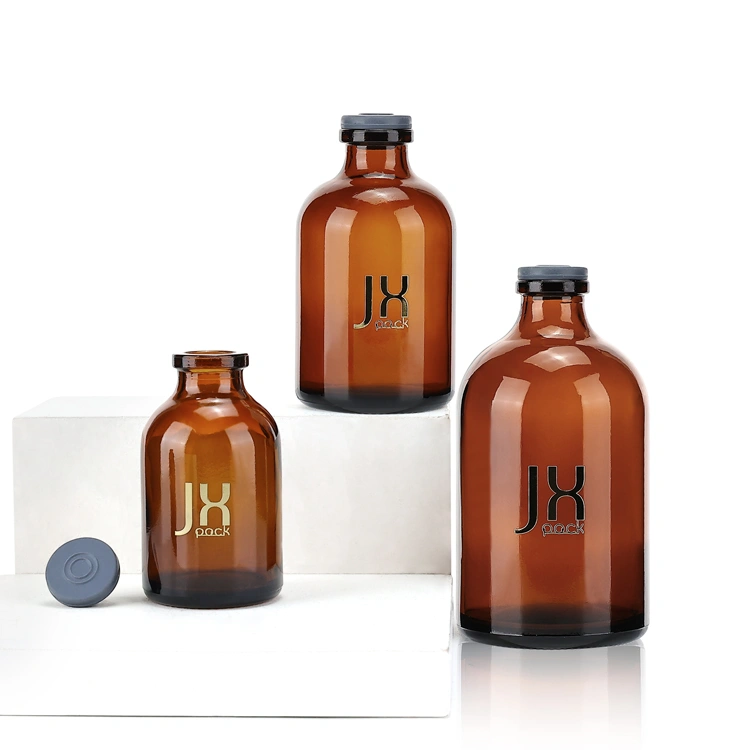
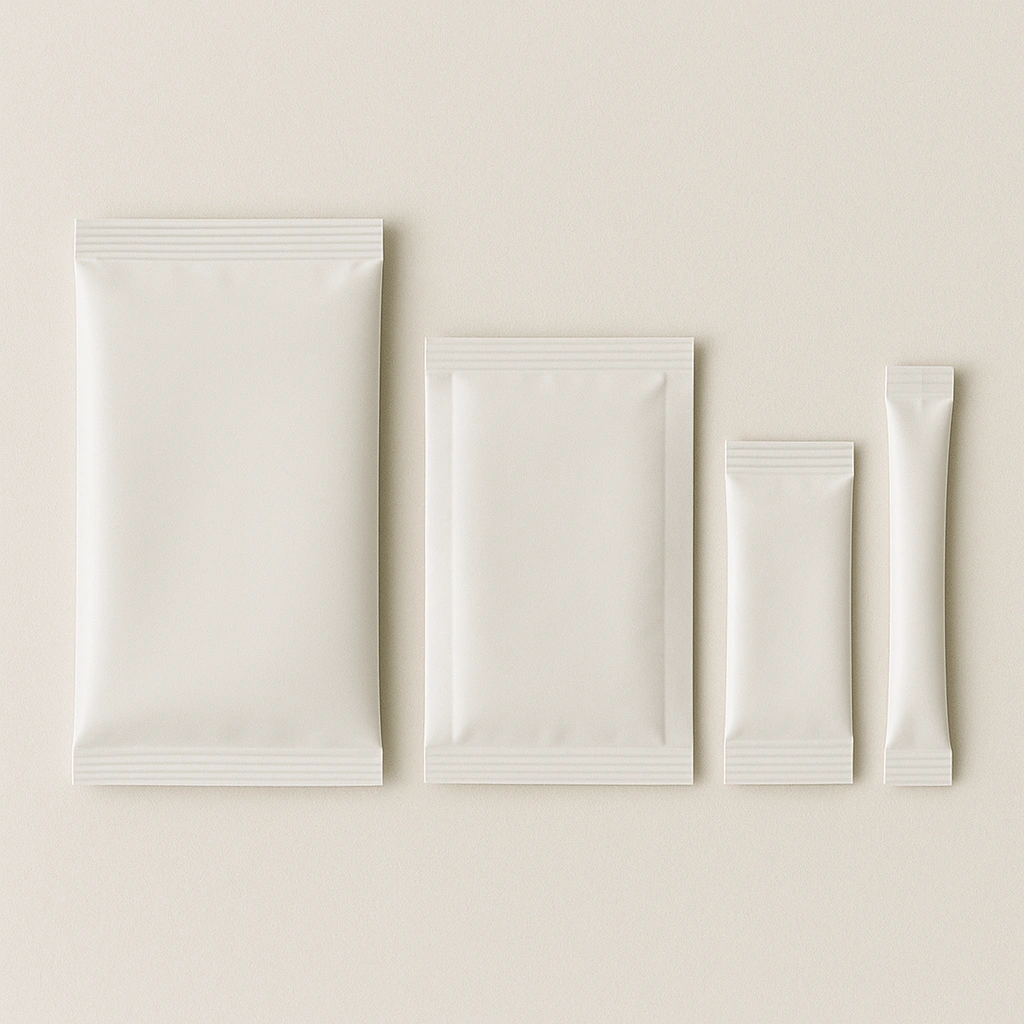
· LATEST DESIGN
The world’s go-to cosmetic packaging factory for custom branding. Talk to Jarsking Team