The 'S' in ESG - A New Paradigm for China's Workforce
The social dimension of corporate responsibility in China has matured from a peripheral concern into a central pillar of sustainable business strategy. This evolution is not a spontaneous corporate awakening but the result of a powerful combination of regulatory pressure and a fundamental shift in workforce expectations. Companies are discovering that investing in their people is no longer just the right thing to do; it is a critical driver of performance, innovation, and long-term value.
The Regulatory Push and Market Pull
- The Amended Company Law: Effective July 2024, this law provides a strong legal foundation for ESG governance, explicitly requiring companies to consider the interests of all stakeholders, including their employees.
- Mandatory Disclosure Rules: Stock exchanges in Shanghai, Shenzhen, and Beijing are phasing in mandatory sustainability reporting, with full implementation for many listed companies expected by 2026. This creates a new standard of transparency and accountability.
| Social Dimension | What It Means (Updated) | Key Metrics Used in ESG Evaluations (2024–2025) | Examples of What Companies Must Do |
|---|---|---|---|
| Labor Practices & Fair Working Conditions | Ensuring workers are treated fairly and protected | • % of employees covered by collective bargaining• Lost-Time Injury Frequency Rate (LTIFR)• Average wages vs. local living wage• Overtime hours compliance | • Implement ISO 45001 safety system• Prove living-wage compliance• Provide PPE and safety training |
| Human Rights & Ethical Sourcing | Protecting rights across operations and supply chains | • Supplier social audits passed (%)• Forced labor risk score• Child labor prevention controls• Responsible minerals sourcing reporting | • Audit Tier 1–3 suppliers• Enforce no-child-labor clauses• Verify cobalt/mica supply chains |
| Diversity, Equity & Inclusion (DEI) | Ensuring equal opportunity and diverse representation | • Gender ratio in management• Pay equity ratio (male/female)• % of underrepresented groups hired/promoted• Anti-discrimination training completion | • Publish pay-gap report• Set DEI targets• Conduct annual bias-reduction training |
| Employee Health, Safety & Well-Being | Providing a safe, healthy, supportive workplace | • Absentee rate• Workplace injury rate• Employee satisfaction score• Mental-health benefit usage | • Offer mental-health programs• Provide ergonomic assessments• Create anonymous safety reporting channels |
| Training & Human Capital Development | Long-term investment in employee skills | • Training hours per employee• Career progression rate• Internal promotion vs. external hiring ratio | • Establish learning platforms• Sponsor certifications• Provide skill-upgrading subsidies |
| Community Relations & Social Impact | Contribution to local communities where business operates | • % of profits donated• Community engagement hours• Local hiring rate• Public complaints resolved (%) | • Build local employment programs• Support schools/health clinics• Engage with community councils |
| Product Responsibility & Consumer Safety | Protecting customers and ensuring product integrity | • Number of product recalls• Customer data breach incidents• Compliance with safety certifications (e.g., FDA, CE, ISO) | • Implement data encryption• Conduct batch-level testing• Publish safety documentation |
| Supply Chain Labor Standards | Ensuring partners follow proper labor standards | • Supplier ESG risk score• Audit findings closure rate• High-risk supplier dependency (%) | • Require supplier code of conduct• Perform annual audits• Redirect sourcing away from violators |
| Privacy, Data Protection & AI Ethics (New Focus 2024–2025) | Responsible handling of customer and employee data | • Number of privacy incidents• GDPR/CCPA compliance status• AI fairness and bias audits | • Implement AI-ethics guidelines• Appoint data protection officer (DPO)• Conduct annual penetration tests |
The “S” in ESG, 2025 Global Standards
From Compliance to Proactive Investment in Employee Welfare
| Well-being Dimension | Key Corporate Concerns & Initiatives |
| Mental Health |
A top concern for 56% of companies, leading to the rise of Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs) and dedicated mental health support |
| Work-Life Balance |
In response to issues like the now-banned “996” culture, 83% of Chinese enterprises now offer flexible options like remote work to combat burnout, which remains a concern for 46% of firms |
| Social Health |
Companies are fostering a positive work environment through team-building and cultural activities, recognized as key to easing pressure and building loyalty |
| Financial Health |
Fair wages, social security, and comprehensive benefits are foundational. Some firms, like ride-hailing giant Meituan, are extending these protections to gig workers with social security subsidies |
Leading companies are putting these principles into practice. CLP China, for instance, launched a comprehensive “Work-Life Coaching Programme” that provides resources on physical, mental, social, and financial health, earning it external recognition for innovation.
Career Advancement as a Cornerstone of Social Responsibility
The Employee Experience at Jarsking
While large corporations like JD.com set national benchmarks, the true test of the ESG movement lies in its adoption by specialized, growth-oriented companies. Jarsking, a global packaging manufacturer founded in 2003, serves as a powerful case study of these principles in action. Evolving from a trading operation into an integrated manufacturer with a global footprint, Jarsking credits its success to a deeply ingrained “people-first” ethos. The company’s approach to talent management is not an afterthought or a compliance measure; it is the engine of its innovation and growth.
Architecting Careers - Advancement at Jarsking
At the heart of Jarsking’s talent philosophy is the belief that organizational success is a direct result of its people’s collective expertise. The company has therefore built a sophisticated and multi-layered system designed to cultivate well-rounded, versatile professionals and provide them with clear, structured pathways for growth. This system moves far beyond the traditional annual review, creating a dynamic ecosystem of continuous learning, mentorship, and opportunity.
Structured Pathways for Growth
- Structured Rotational Programs: For new graduates and early-career professionals, Jarsking offers 12-18 month rotational programs. Participants gain invaluable, hands-on experience across multiple core departments, such as sourcing, manufacturing, and sales. This holistic exposure ensures they understand the entire value chain, from initial concept to final delivery, and helps them identify the career path that best suits their skills and interests.
- Continuous Learning Culture: The company fosters an environment where learning never stops. It organizes regular technical workshops, industry trend briefings, and internal knowledge-sharing sessions. This ensures that every team member, from engineers to sales professionals, remains at the forefront of emerging technologies, sustainable materials, and market developments.
- External Collaborations: Recognizing the value of outside expertise, Jarsking partners with technical institutes and industry associations. These collaborations provide employees with specialized training in high-demand areas like sustainable packaging materials, advanced decoration techniques, and international quality management systems, bringing fresh perspectives directly into the organization.

A Framework for Mobility, Feedback, and Mentorship
- Internal Mobility: Jarsking actively encourages employees to move between its five specialized factories (Mold, Glass, Plastic, etc.) and its various functional departments. This policy is designed to build a uniquely versatile workforce. An engineer who has spent time in sales understands client needs more intuitively; a sales manager who has worked in logistics can make more reliable delivery commitments. This cross-pollination of skills creates a deeply integrated and adaptable team.
- Monthly Performance Feedback: In a significant departure from the standard corporate practice of annual reviews, Jarsking managers conduct monthly performance evaluations. These brief, regular assessments create consistent touchpoints to track goal achievement, recognize contributions, identify growth areas, and provide coaching. This ensures that development is an ongoing conversation, not a once-a-year event, keeping employees and managers continuously aligned on objectives and progress.
- Global Opportunities: As a company with a growing international presence—including offices in the USA and UAE—Jarsking offers tangible global career paths. The active recruitment for senior remote roles, such as the “Vice President Strategic Partnerships,” demonstrates a clear route for ambitious employees to gain international experience and take on leadership responsibilities on a global scale. This transforms a job into a global career, providing a long-term vision for professional growth within the company.

Fostering Community - Welfare and Culture at Jarsking
Jarsking understands that a successful career is built not just on skills and promotions, but also on a sense of belonging and well-being. The company’s investment in its people extends far beyond the professional sphere, creating a vibrant, supportive, and engaging corporate culture that serves as the social fabric of the organization. This focus on community is not a “soft” perk; it is a strategic tool for enhancing employee loyalty, reducing burnout, and fostering the collaboration necessary for innovation.
A Culture of Collaboration and Engagement
This culture reveals itself most clearly on the global stage. At trade shows around the world—from Cosmopack Asia in Hong Kong to Cannafest in Prague—Jarsking’s team brings an unmistakable sense of energy and unity. The scenes are always similar: a buzzing booth, teammates moving in sync, and an atmosphere that feels more like a shared mission than a work assignment.
Celebrating People, Building Community
- Annual Company-Wide Travel: A significant investment in team cohesion, this annual trip allows employees from different departments to connect in a relaxed, informal setting, building relationships that translate into smoother collaboration back at the office.
- Celebrations for Traditional Festivals: By marking important cultural holidays together, Jarsking reinforces a sense of shared community and respect for tradition.
- Monthly Birthday Parties: This simple but consistent gesture ensures that every individual feels seen and celebrated. It transforms the workplace from a collection of employees into a community of people.
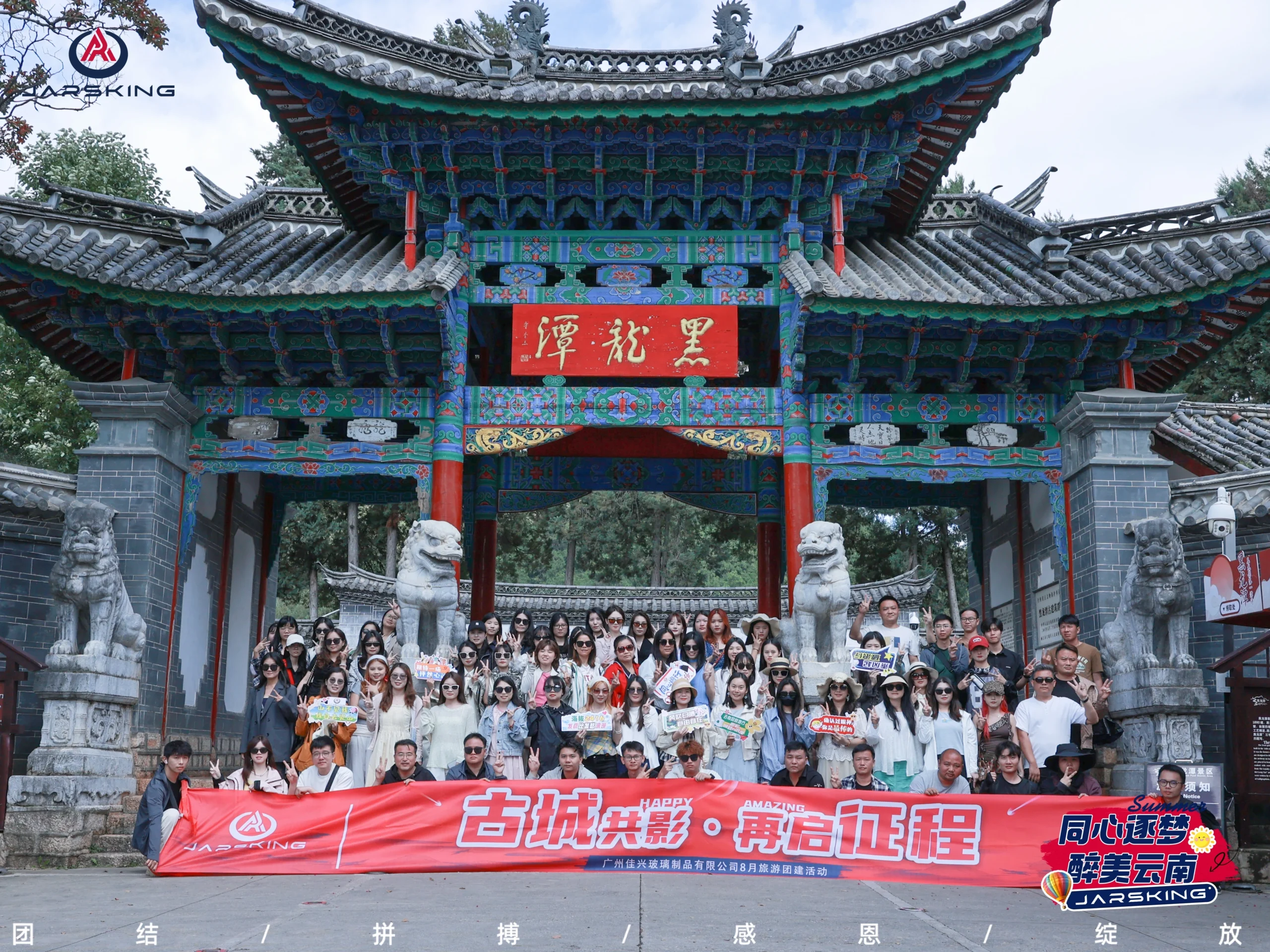
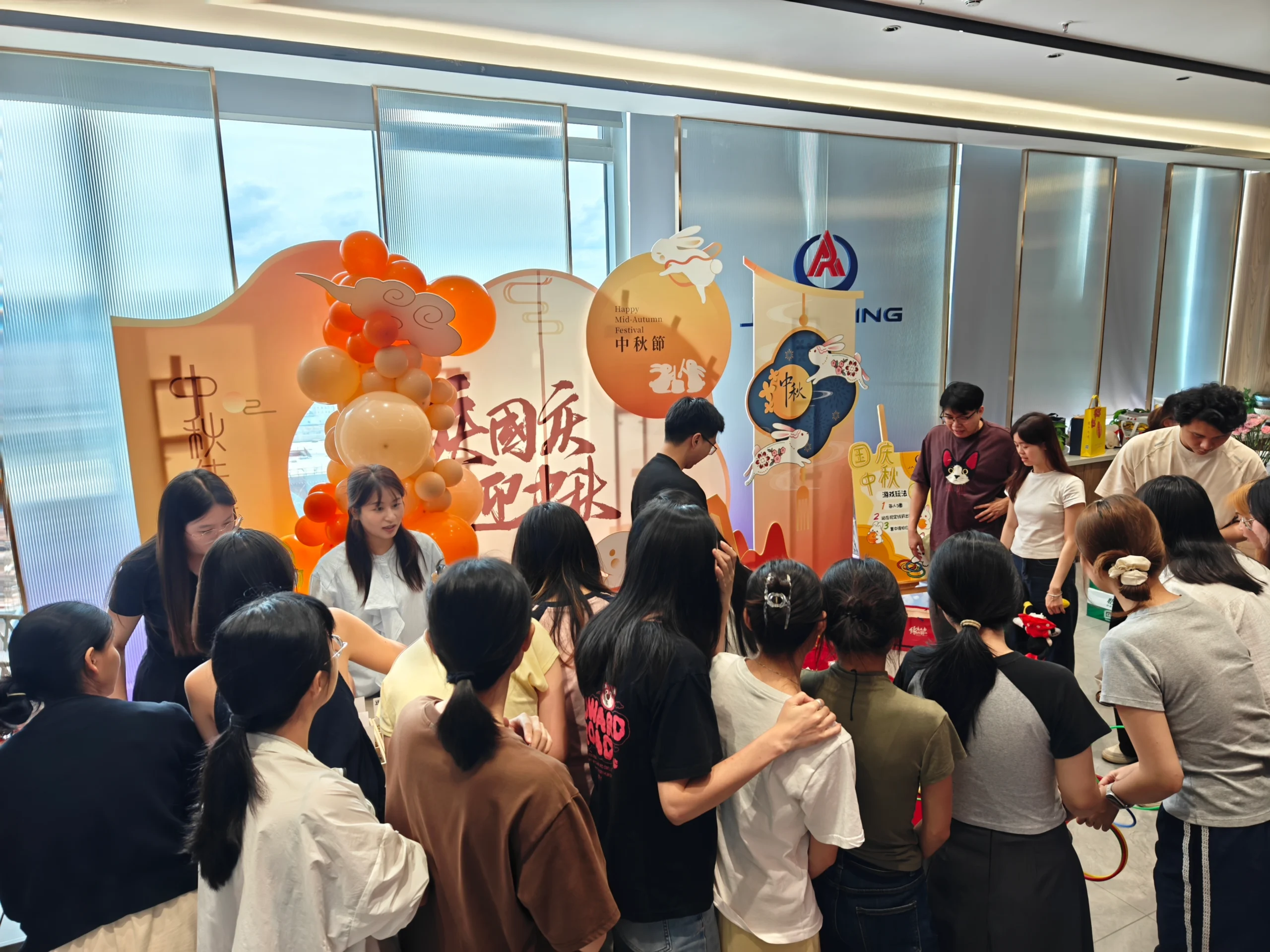




Synthesis & Broader Implications
Jarsking’s employee-centric model is an execution of the macro-level ESG trends sweeping across China. By drawing direct lines between the company’s specific practices and the national data, we can see how Jarsking serves as a practical blueprint for how to successfully integrate the ‘Social’ pillar into a business strategy, transforming it from a compliance burden into a formidable competitive advantage.
Connecting the Micro to the Macro
- Human Capital Development: The national trend shows a heavy emphasis on robust training programs, with industry giants like JD.com setting a high bar. Jarsking’s multi-faceted approach—combining structured rotational programs, continuous learning workshops, and external collaborations—is a direct and sophisticated implementation of this principle. It demonstrates a commitment to building human capital that is both deep in expertise and broad in perspective, creating a workforce that is not just trained but truly developed.
- Holistic Employee Well-being: Research shows that Chinese companies are increasingly concerned with mental health, burnout, and the overall work environment, with 31% identifying the latter as a key well-being concern. Jarsking’s focus on a vibrant, collaborative culture—evidenced by its team-building travel, company celebrations, and the energetic atmosphere at its trade show booths—directly addresses this. These initiatives are not peripheral perks but are central to fostering the positive social and mental environment that ESG frameworks now demand.
- Purpose-Driven Workplaces: The modern workforce, especially in China, is looking for more than a paycheck; they seek purpose and a clear vision for their future. Jarsking’s commitment to internal mobility, its clear pathways to leadership, and its global opportunities provide exactly that. An employee can join as a graduate in a rotational program and realistically envision a future as a department head or even a partner leading an international office. This creates a powerful retention tool and fosters a deep sense of loyalty and shared purpose.
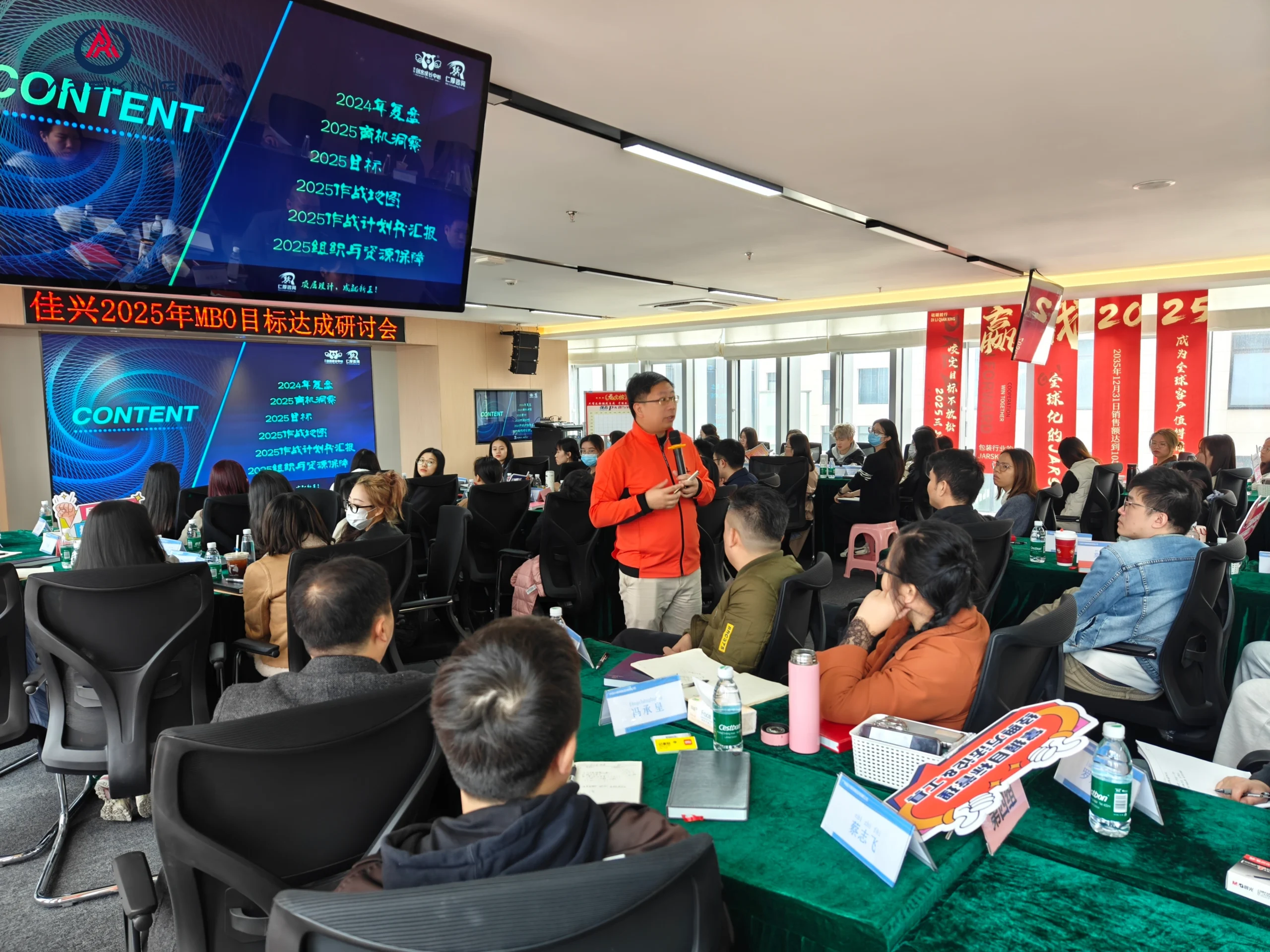

Jarsking as a Model for the 'S' Pillar
- Investment in a world-class R&D team with continuous training directly fuels its capacity for innovation, allowing it to live up to its promise of “New Designs Every Day”.
- Investment in a globally distributed and highly trained sales team is the engine of its successful international expansion into North America, Europe, and the Middle East.
- Investment in a positive and engaging culture makes the company a magnet for top talent in a competitive market, creating a sustainable competitive edge that is difficult for rivals to replicate.
Broader Implications for the Future of Work in China

Conclusion
FAQs
China’s ESG framework has seen a dramatic rise in the ‘Social’ pillar, with companies receiving high ratings (BBB or above) for social performance jumping from 23.6% to 65.8% as of 2024. This reflects a move from compliance to proactive investments in holistic well-being, driven by regulations like the Amended Company Law (effective July 2024) and mandatory sustainability reporting by 2026.
Younger employees and investors are pushing for purpose-driven workplaces, leading to benefits like 25% lower turnover and 18% higher productivity for ESG-focused firms. For those passionate about corporate social responsibility, this trend signals a more humane, innovative future of work in China.
Under the evolving ESG ‘S’ pillar, 77% of HR departments now integrate ESG into benefit packages, focusing on mental health (a priority for 56% of firms via Employee Assistance Programs), work-life balance (83% offering flexible options like remote work to counter burnout), social health through team-building, and financial security with fair wages and subsidies.
Examples include CLP China’s “Work-Life Coaching Programme” for comprehensive health support. This shift not only complies with rising labor disclosures (from 58% to 72% in reports) but builds loyal, resilient teams—ideal for CSR enthusiasts eyeing sustainable career paths in China.
Career development is now a cornerstone of ESG, with new guidelines mandating reports on training mechanisms, viewing human capital as vital for sustainable growth amid China’s “dual carbon” goals. Demand for green jobs, like ESG specialists, surged 38% in six months, creating talent gaps that companies address through upskilling—e.g., JD.com’s 54.44 average training hours per employee in 2021. This fosters loyalty and innovation, turning career programs into strategic assets. For ambitious professionals, it’s an exciting opportunity to advance in purpose-driven roles while contributing to national economic transformation.
Jarsking builds careers through structured rotational programs (12-18 months across sourcing, manufacturing, and sales for new graduates), continuous learning via workshops and external partnerships on sustainable materials, and internal mobility between its departments. This people-first approach equips employees for versatile growth, making Jarsking a prime spot for those seeking dynamic career opportunities in China’s ESG-aligned manufacturing sector.
Jarsking’s vibrant culture emphasizes community to combat burnout, with annual company-wide travel for team bonding, monthly birthday parties, and traditional festival celebrations that build belonging. These initiatives align with ESG trends by enhancing mental and social well-being, creating a loyal, innovative workforce. CSR-focused readers will appreciate how this turns the workplace into a thriving community hub in China.